GALOCE (China) - The load cell is actually a device that converts the quality signal into a measurable electrical signal output. When using a sensor, we must first consider the actual working environment in which the sensor is located. This is very important for the correct selection of the load cell. It is related to the normal operation of the sensor, its safety and service life, and the reliability and safety of the entire weighing instrument. Sex. In the basic concepts and evaluation methods of the main technical indicators of the load cell, there are qualitative differences between the new and the old national standards.
Judgement of the quality of the load cell:
Weighing equipment may have inaccurate weighing after long-term use. Generally, we have to solve these problems through the calibration of the weighing controller. But sometimes the scale body cannot be restored to normal no matter how it is calibrated. At this time, we have to investigate in detail from all aspects of the weighing mechanism, and the core component of the weighing mechanism is the load cell.
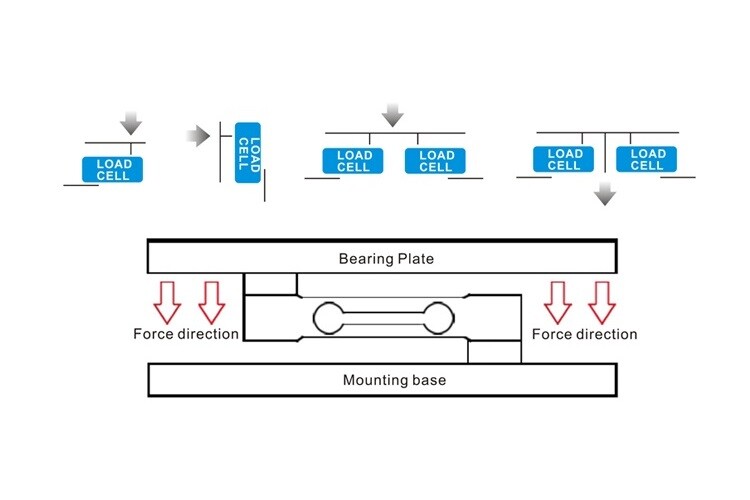
Current weighing equipment generally uses resistance strain gauge load cells (analog) as the core component of the weighing mechanism. It uses the Wheatstone bridge principle to convert the weight signal into a linearly changing electrical signal. There are conventionally four lines, and the input is 5-10V excitation voltage (supply voltage), the output is a weight signal with "mV" as the unit. The following editor will show you how to judge the quality of the load cell:
One: Observation:
Observe whether the sensor is deformed or cracked. If these conditions occur, you need to contact the manufacturer to replace a new sensor.
Two: Line input and output measurement method:
Find the sensor connection terminal in the weighing controller (weighing instrument), and determine the sensor connection circuit
Under normal circumstances, the excitation voltage (between EXC+ and EXC-) is 5-10V, and the output voltage (between SIG+ and SIG-) is close to 0 when the device is empty, which is less than the maximum output of the sensor. (The maximum output of the sensor = excitation voltage * sensor sensitivity, the sensitivity of the checkweigher sensor is mostly 2mV/V), if it exceeds this range, contact the service provider to apply for a replacement of the sensor.
Three: Sensor resistance measurement method:
Measure the resistance of the sensor, and judge the quality of the sensor by the resistance
1: Input resistance≧output resistance>bridge resistance
2: Under normal circumstances, the bridge resistances are equal or equal to each other
(Note: The input resistance is the resistance between EXC+ and EXC-, the output resistance is the resistance between SIG+ and SIG-, and the bridge resistance is from EXC+ to SIG+, EXC+ to SIG-, EXC- to SIG+, EXC- to SIG- Resistance between)
The above is the judging method of the load cell in the weighing equipment. It should be noted that the load cell is not so easy to be damaged under normal use. Many failures are caused by the improper use of the scale body to overload the load cell. Therefore, in the process of using and disassembling and maintaining the weighing equipment, we should try our best to avoid heavy object impacts and bumps, and operate strictly in accordance with the weighing range of the equipment.
Analysis of five common causes of errors in load cells:
Then the load cell will inevitably produce errors in use, and what types of errors will the load cell have? What causes the error?
1. Characteristic error. It is caused by the device itself, including the DC drift value, the incorrect slope or the non-linear shape of the slope. After all, there will be a gap between the ideal transfer function characteristics of the device and the real characteristics.
2. Application error of load cell. That is, errors caused by operation, including incorrect placement of probes, incorrect insulation between the probe and the measuring location, errors in the purification process of air or other gases, incorrect placement of transmitters and other operating errors. The error.
3. Dynamic error. Sensors suitable for static conditions will have strong damping, so the response to changes in input parameters is slow, and it may even take several seconds to respond to a step change in temperature. Some load cells with delay characteristics will produce dynamic errors when responding to rapid changes. Response time, amplitude distortion, and phase distortion all cause dynamic errors.
4. Insertion error. It is the error caused by changing the measurement parameters when a sensor is inserted into the system. Using a transmitter that is too large for the system, the dynamic characteristics of the system is too slow, and the self-heating in the system loads too much heat, etc., will cause insertion errors.
5. Environmental error. The use of the load cell is also affected by the environment such as temperature, swing, vibration, altitude, chemical substance volatilization, etc. These factors are very easy to cause environmental errors.



























Interested? Submit your enquiry using the form below:
Only available for registered users. Sign In to your account or register here.